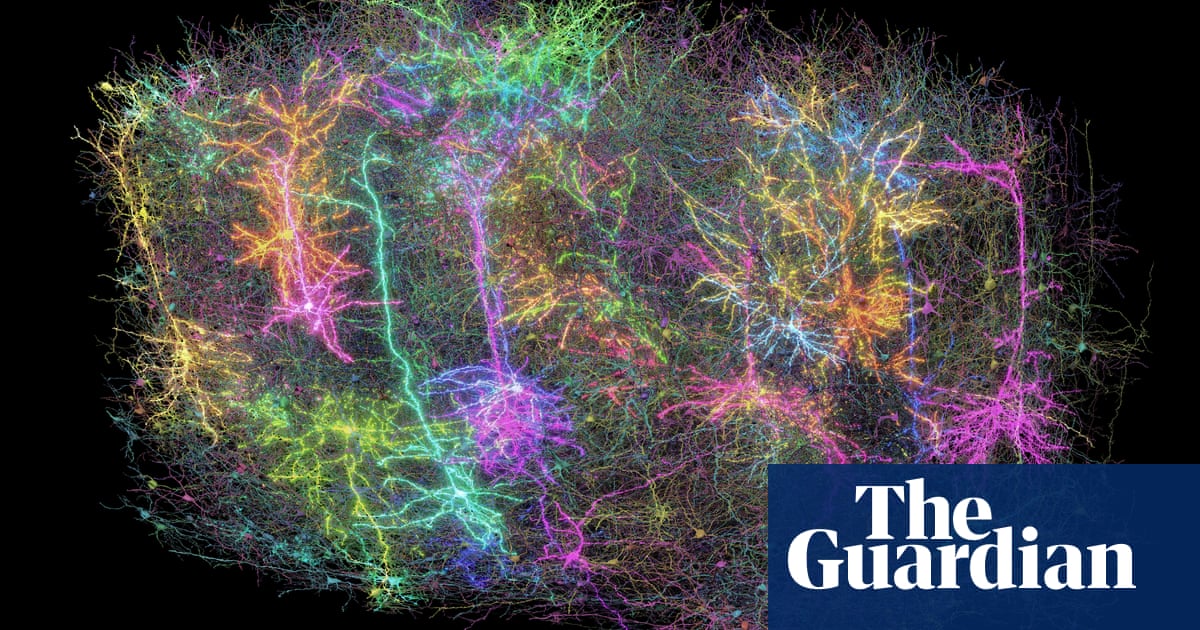
Scientists have made a remarkable breakthrough by creating the most detailed circuit diagram of neurons in a mammal’s brain. This map focuses on a tiny part of a mouse’s visual cortex, tracing the connections of 84,000 neurons and half a billion synapses over approximately 5.4 kilometers of wiring. This work opens up new avenues for understanding how our brains function and how various types of cells collaborate. It could lead to insights into complex conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, autism, and schizophrenia.
Dr. David Markowitz, a neuroscience expert, likened this advancement to the Human Genome Project. He believes its potential to revolutionize our understanding of the brain is immense. The MICrONS project aimed to not just map neuron structures but also to explore the electrical communication between them, revealing the intricate conversations that occur in our brains.
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine used advanced microscopes to observe brain activity while mice watched different videos. They then sliced a cubic millimeter of brain tissue into over 25,000 ultra-thin sections, each about 1/400th the width of a human hair. High-resolution images of these slices were captured using electron microscopes.
At Princeton University, artificial intelligence was employed to piece together the cells and their connections in 3D, resulting in a massive dataset totaling 1.6 petabytes—about the equivalent of 22 years of nonstop HD video.
Dr. Clay Reid from the Allen Institute described the tiny sample as a complex architecture, akin to a forest. He emphasized that this reconstruction allows scientists to revisit old theories and uncover new insights about brain functions.
Crucially, this research has uncovered new types of brain cells and a fresh understanding of how inhibitory cells work. Unlike previous beliefs that they merely suppress activity, the latest findings show that these cells are selective about their targets, leading to a coordinated network that enhances brain function.
Understanding the layout and workings of the brain can improve our grasp of brain disorders involving neural communication issues. Dr. Nuno da Costa highlighted the value of having this "circuit diagram," suggesting it could aid in diagnosing and treating brain-related diseases by comparing healthy brain wiring to that of affected ones.
This exciting research is detailed in a series of papers published in the journal Nature. It’s a significant step forward in neuroscience, shedding light on the complex operations of the brain and providing hope for future advancements in treating neurological conditions.